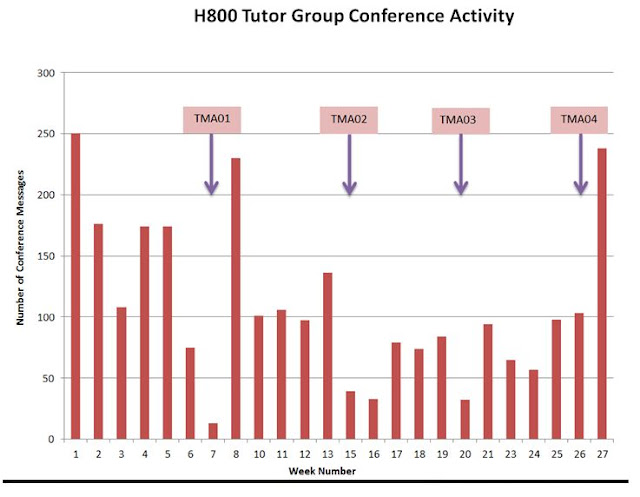
Fig.1. The consequences of an activity system - loads of action. Here a tutor group over a period of 27 weeks. 'Activity' is represented by messages in a tutor forum. H810 is an Open University postgraduate course in Education. Technology-enhanced learning: practices and debates
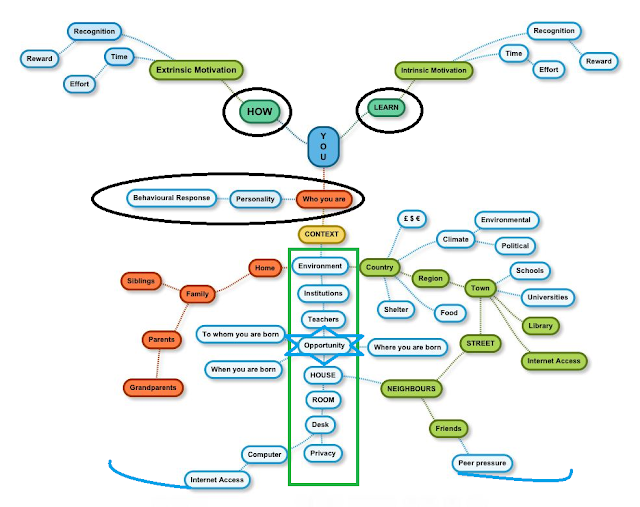
Visualizing actions between people, concepts and things required more than words - models and metaphor start to create meaning.
Why use any model?
A model should be a well-founded visual simplification of an aspect of a complex reality that communicates its concept clearly, is based on thorough research, and is easily shared for feedback and review. Users should find that a model, like an experiment, is repeatable so that in time a body of work including case studies and a critique of the model builds credibility. A conceptual model such as an Activity System is ‘particularly useful when one wants to make sense of systemic factors behind seemingly individual and accidental disturbances, deviations, and innovations occurring in the daily practices of workplaces’. Engeström (2008:27)
Conole and Oliver (2011) mention four levels of description:
1. Flat vocabulary
2. More complex vocabulary
3. Classification schemas or models
4. Metaphors
The vocabularly is inevitable, though talking this through to an audience would be my prefered approach, so that with engagement reponse is invited. The models used here, from Vyogtsy and Leon'tev to Engestrom may appear familiar and set - they not. There is a group that likes to see everything 'triangulated' - diamonds and stars, though evident in the literature on education - maybe akin to complex rather than plain language. From models we move to various metaphors - and you are certain to have your own. While Engeström himself moves on to ideas of 'knotworking' and fluid, organic representations.
Engeström (1987) took a current model - that of Vygotsky (1978) and made it his own and has since offered a metaphor to explain it further.
Why use an Activity System?
Activity Systems derive from a century of analysis of the way people construct meaning (Vygotsky, 1978. Leon’tev, 1978) that later researchers applied not simply to how people think, but how groups of people (Engeström, 1987) act in collaborative ways.
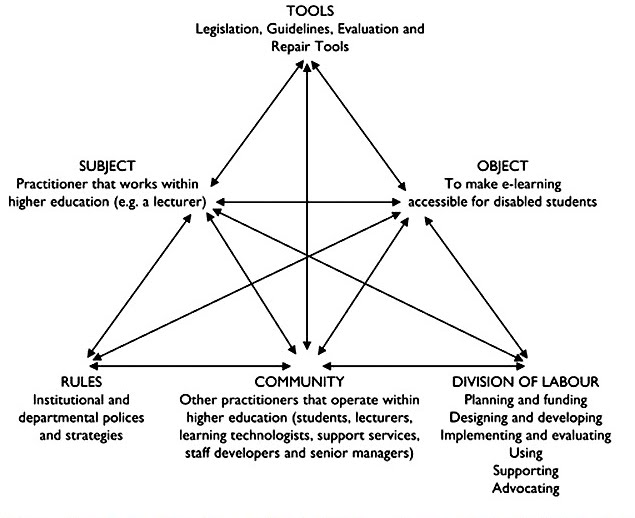
Fig.2. Application of Engeström’s (1987) systemic model of activity featured in Seale (2006)
There are two parts to an Activity System - upper and lower. The upper part is the triangle drawn to represent the interaction of Subject, Tools and Object.

Fig. 3. Vygotsky.L.S. (1978) from Mind in Society.
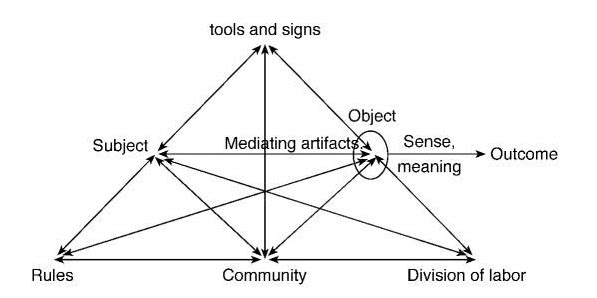
Fig.4. The structure of a human activity system. Engeström 1987.
Historically this is where Vygotsky began in Moscow in the late 1920s (Fig.3) Engeström and others turned the experssion of Vygotsky's model the other way up. This split of upper and lower serves another purpose - Yrjö Engeström likens this expression of an activity system to an iceberg where the top triangle - Subject - Tools - Object is what we see, while the other actions, that give the system context - he added when developing Vygostky’s (1978) original model, are beneath the surface. Engeström. (2008:89). (Fig.4) It's worth remembering that Vygotsky was working on how people create meaning, while later thinkers have adapted this to help scrutinise how communities or groups of people, tools and sets of guidelines create (as Engeström puts it above, 'sense meaning' Engeström 1987).
When is the construction of an Activity System useful?
Engeström (2008:27) suggests that it is particularly useful ‘when one wants to make sense of systemic factors behind seemingly individual and accidental disturbances, deviations, and innovations occurring in daily practices of workplaces’. Someone needs to think it is necessary to study the status quo - perhaps because there is an awareness that something, somewhere is going wrong, or that there has been an actual downturn in business or collapse in profitability, or a desire simply to look at things in a different way to understand where improvements can be made, a change in policy and law, or a reinvented or renewed.

Fig. 5. Engeström.Y (2008) From Teams to Knots: Activity-theoretical studies of Collaboration and Learning at Work.
Engeström (2008:207) suggests that there are five principles in relation to theories of activity systems.
- Object Orientation
- Mediation by tools and signs
- Mutual constitution of actions and activity
- Contradictions and deviations as source of change
- Historicity

Fig. 6 A White Knight from a Lewis Chess Set (replica) playing the role of the Object - the purpose, motivation and idea behind the activity in the system through whom sense is made or an outcome is derived.
1) Object Orientation
The Object is a problem, the purpose, the motivation and opportunity - the modus operandi behind the activity. ‘Object orientation’ (Engeström 2008:222) is a crucial prerequisite of working with an activity system. In the context of accessible e-learning Seale (2006:165) creates an Activity System in which the object(ive) is ‘to make e-learning accessible for disabled students’. As an exercise considering its widest application this object definition suffers because the object is so broad it embraces a myriad of issues and circumstances, each word is open to interpretation - what, for example, is meant by ‘e-learning’, what is meant by ‘accessible’ by ‘disabled’ and by ‘student’. Rather than an object as an opportunity or goal as Seale uses, a fix, the desired outcome, is more likely to be found where, at least in the first instance, we identify a particular context and a tightly defined problem.
Not only that, but to contain the likelihood of ‘ruptures’ across the activity system clarity and agreement is required on the problem that needs to be fixed. In relation to accessibility to e-learning for students with disabilities there are multiple problems, many unique to a student with a particular disability or, where feasible and appropriate, a group that can be identified by the nature of their disability, for example, deaf students who are seen as, and many want to see themselves as a ‘minority language’ group. What is more, a disabled student may have several impairments and the degree to which these are a barrier to e-learning is fluid, perhaps ameliorating with treatment, or getting worse, transmogrifying, or simply being intermittent. As these are known issues that would cause problems or clashes within the activity system and prevent its working it seems futile to build an activity system on this basis - knowing that it will fail.
‘A problem well stated is a problem half-solved’. (Charles Kettering)
This may be an aphorism, but it rings true. Problem scoping is necessary but where a problem remains elusive, or is ‘messy’ rather than ‘tame’ (Rittel and Webber's 1973, Ackoff 1979, Ritchey 2011) a variety of creative problem solving techniques (VanGundy, 1988. Griggs, 1985). Knowing what the problem is enables innovation - identifying the problem and devising a fix, and in communications, where, for example, advertisers prepare a creative brief that begins by clearly identifying the problem.
‘Object orientation’ and in this context, problem definition and refinement, is the first in five principles set out by Engeström (2008:207) for using activity systems. The drive, purpose and motivation for all the actions between the six identified nodes depends on the object ‘that which is acted upon’. A key component of activity theory is the transformation of this object into an outcome i.e. to solve the problem. If solving a problem is the goal, and recognition of a successful enterprise undertaken, then all the more reason to get the definition of the object correct - the process can be repeated for different problems, at different scales and over time. Without absolute clarity over the object you may find that different people in the system have differing interpretations of what it is. Kuutti (1996) found that having more than one object under scrutiny was a reason for an activity system to fail. An answer where there are two distinct problems may be to treat them as such and attach them to separate activity systems. Whilst for the sake of scrutiny it is necessary to isolate an activity system, they do of course interact - indeed it is by looking at how two activity systems interact that you may reveal how problems are solved or innovations produced. However, if the object is wrong, or ill-defined or ambiguous then the motives may be out of kilter and it would therefore be necessary to transform all of the components of the activity system, especially and including those at the bottom half of the ‘iceberg’. Engeström (2008:87)

Fig. 7. The black Queen from a Lewis Chess Set representing 'Tools'
2) Mediation by Tools and Signs
Tools might be evaluation and repair tools and assistive technologies, software or legislation, guidelines or staff development. Tools are a mediating factor between the Subject (student, lecturer, facilitator of the desire outcome) and the Object - the purpose of all this activity.
Tools play a significant role in the history of tackling accessibility issues, to undue, out do or transform resources or interpret platforms in a way that communicates their meaning offering some if not all the affordances of the tools as designed for students, who, having gained a place to study a degree in Higher Education might be thought of as some the most able’, not simply the ‘able’.Tools in this role at the apex of the Activity System and can include guidelines and legislation where they are an applied ‘tool’ rather than a rule or standard. ‘ A functioning tool for the analysis of teams and organisations’. Engeström (2008:229) Of course the category includes evaluation and repair tools, assistive technologies and software and equipment. Tools ‘mediate’ between the Subject - the facilitator of change through activity and the outcome of the activities - the Object. ‘To build a website that complies to level AAA’ may be achievable whilst ‘to make e-learning accessible for disabled students’ Seale (2006 sounds like wishful thinking, rather ‘to build an e-learning module that when scrutinised by a representative range of people with dyslexia’ receives a grading of ‘satisfactory’ or above’. This would suggest the involvement therefore of dyslexic students in the testing of a navigation interface for the virtual learning environment as an ‘action’ between subject and object.
sounds like wishful thinking, rather ‘to build an e-learning module that when scrutinised by a representative range of people with dyslexia’ receives a grading of ‘satisfactory’ or above’. This would suggest the involvement therefore of dyslexic students in the testing of a navigation interface for the virtual learning environment as an ‘action’ between subject and object.
There is a particular congregation of ‘contradictions’ stemming from the relationship between Tools and both Subject and Object:
- The array of design and evaluation software applications (Seale, 2006)
- The mastery of external devices and tools of labour activity (Nardi, 1996)
- No rules of practice for use of that tool (Isscroft and Scanlan, 2002 )
- Tools that are overly prescriptive (Phipps et al, 2005)
- How do you choose from amongst such a plethora of tools?
- The context in which tools are introduced (Seale, 2006:160)
3) Mutual constitution of actions and activity
The links between each component - object, tool, subject and so on - should equate to a burst of electricity or perhaps a chemical induced response between a synapse and a neuron - Engestrom (2008) goes as far as to liken an activity system to a type of fungi - mycorrhizae like formation Engestrom (1997).

Fig.8. Mycorrhizae - one way Engeström sees an Activity System
An Activity System should be seen not as a concept of a static entity, but rather a living and growing thing. The actions, the double-arrows between each concept, are what gives an activity system structure - it’s the management of the disturbances, contradictions and conflicts along these lines of action that disturb effective flow where the role of an activity system comes in - identify then fix these and you move towards achieving the object orientation or outcome. Knorr-Cetina (2003) talks of 'flow architecture' and if neither of these concepts ring true for you in realtion to activity systems then Zerubavel (1997) talks of 'a mindscape' while Cussins (1992) talks of 'cogntive trails'.
4) Contradictions and deviations as source of change
I would have opted for Subject as the third issue, but reading Engeström made me think again. Subject, Tools, Object reduces the Activity System to the far simpler upturned triangle Vygotsky devised to explain how people create meaning (Vygotsky, 1978:86) without further thought to the deeper and wider issues once learning is put in context, that Engeström (1987, 2008, 2011) added by broadening this way of showing how ‘meaning is created’ in the workplace by adding Rules, Community and Division of Labour.
Rather than picking one more of these concepts at the expense of leaving the others out I think that the ‘Actions’ the double arrows that indicate something happening between the elements is of interest. I believe this would be the fourth of Engeström's five principles - Contradictions and deviations as source of change. This after all is, literally, where all the ‘action’ takes place, what Seale (2006:164) describes as ‘problems, ruptures, breakdowns or clashes’. (I need to go back and to understand what is meant by Engeström's third principle - ‘Mutual constitution of actions and activity’) I think this is the principle that the Activity System has to be seen as a complete, self-contained entity, that any break or failure or misunderstanding in the system would call it to fail so you’d be better of starting again from scratch until the scale or context works. Engeström uses the metaphor of a very particular kind of lichen (‘mycorrhizae’, Engeström, 2008:229) to describe Activity Systems - he doesn’t suggest however that you attempt to work with this kind of complexity, rather it is a reminder that an activity system is fluid and changing and depends on activity taking places between the defined nodes.
5) Historicity
Fig. 9. A discontinuous series of Activity Systems ... like Toblerone at Christmas.
'Historicity' - Engeström's experssion (2008) - is a term referring to 'the historical actuality of persons and events',(Wikipedia, 2012) suggests the need to see an Activity System as a snapshot, a sequence and a discontinuous one at that. So take the familiar equilateral triangle of the Activity System model and run a line of them. Seale (2006) suggests there is value to be found by doing some 'archaelogy' - I think 'historical research' would be an adequate way to think of it, for what this may reveal about how these 'rupture, conflicts' Seale (ibid) or 'contraditions and devistions as a source or change' Engeström (2008:223) along the lines of activity. Seale (2006) talks of how an activity system 'incesstanly reconstructs itself. Engeström (1994) talks of an ideal-typical sequence of epistemic actgions in an expansive cycle.
Subject
By definition here the ‘non-disabled’, particularly in the cognitive sense though sometimes with athletic promise too. Ironically whilst ‘non-disabled’ is not a favoured term it does at least relate to a homogenous group, while ‘disabled’ does not given the range, scale and potentially shifting nature of impairments to learning from hearing, to visual, cognitive and mobility.
Subject to be of most importance - this is the person, actor or lecturer, indeed a student - anyone who is responsible for facilitating and supporting the student’s learning experience. This may be a practitioner who works with a Higher Education Learning Technologist or the digital media access group if there is such a thing. Engeström (2008:222).
Any of the team members may be a novice, which may be a positive or negative influence for the actions in the system. A novice is inexpert, on the other hand they are free from the habits that may be causing problems and creating barriers. Because of the way a novice learns they are more inclined to innovate as they are not bound or even aware to rules, guidelines and beliefs that may hold them back.
Rules

Fig. 10 A collection of pawns from a Lewis Chess set representing 'Rules'
These can be formal, informal or technical rules. They are institutional and departmental policies and strategies. These are rules of practice, and legislation, as well as strategies and research. They are explicit and implicit norms. These are conventions and social relations. These in the context of accessible e-learning are the various guidelines related to web usability and legislation related to accessibility and equality. Universal Design and User Centred Design are rules too. Rules mediate between the subject and the community. The actions, the 'doing in order to transform something' or 'doing with a purpose' are the activities that link Rules with Subject, Rules with Object and Rules with Community.
Community

Fig. 11. An Activity System represented by chess pieces.This 'Community' comprises the King and two bishops from replica of the Lewis Chess Set.
These are 'people who share the same objective' - their being in this activity system is dependent on their wishing to engage with the object, the opportunity, to strive to achieve the stated outcome. Any ruptures are therefore not a consequence of having the wrong person in this community - this grouping, this loose gathering of like-minded people, is what Engestrom has come to describe as a knot and the actions these people take as 'knotworking' Engeström (2008:194) - latent, informal, sometimes impromptu gatherings of people who assemble to address a problem or to take an opportunity - what Rheingold (2002) describes as 'smart mobs'.
Division of Labor (sic)This concept, or node as an ethereal entity is 'how people are organized to realise the object'. Not one to represent by a chess piece and one may think that this ought to be the link that joins people together ... this is where working with a model as the beat of a heart, not the heart itself, requires acceptance of the way a model is designed to work. Division of labor (US spelling for a Finnish academic ... who has bases in Helsinki and San Diego). This is planning and funding, designing and developing, implementing and evaluating, using, specialists vs. the mainstream).
Conclusion
Digitization of assets is akin to the creation of an ocean in which the binary code are the molecules of water - apt then with the shift from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 and our adopting the use of ‘the Cloud’ and ‘Cloud Computing’ to take this metaphor into a more dynamic form and think of it as a water-cycle. This system is shifting continually horizontally with currents and tides, but also vertically - the exponential growth in computing speeds and memory capacities the energy that drives the system. This global system hasn’t taken adequate account of people with disabilities - as in the real world there are barriers to access caused by visual, hearing, mobility and cognitive impairments - just as these have been addressed in a piecemeal way through legislation, funding, programmes and promotions, by disability groups or holistically, so too with adaptations or changes to the digital world - there is no panacea that will remove all barriers for all people with any disability, of any kind, type or stage of deterioration or amelioration. Stretching the metaphor further I wonder if at times this digital water-cycle, again like the real one, is polluted, that translucence as well as flotsam and jetsam in this ocean are the barriers - on the one hand the pollutants have to be removed - the barriers taken down - but at the same time, cleaner purer water, in the form a universal design that is simpler and usable would gradually cleanse some of system. Once again, a mirror to the real world responses, specialist schools and associations, say for those with dyslexia are blind or deaf, become an oasis or island in this digital system.
‘Those not engaging with technologies or without access are getting left further and further behind. We need to be mindful that the egalitarian, liberal view of new technologies is a myth; power and dynamics remain, niches develop and evolve. Applications of metaphorical notions of ecology, culture and politics can help us better understand and deal with these complexities'. (Conole. 2011:410)
FURTHER READING
Cecez-Kecmanovic, Dubravka, and Webb.C (2000) "Towards a communicative model of collaborative web-mediated learning."Australian Journal of Educational Technology 16. 73-85. Towards a communicative model of collaborative web-mediated learning (last accessed 20 Dec 2012) http://www.ascilite.org.au/ajet/ajet16/cecez-kecmanovic.html
Hardman, J (2008) Researching pedagogy: an acitivty system approach Journal of Education, No. 45, 2008. PP65-95 (last accessed 20 Dec) 2012 http://joe.ukzn.ac.za/Libraries/No_45_Dec_2008/Researching_pedagogy_an_Activity_Theory_approach.sflb.ashx)
Engeström’s (1999) outline of three generations of activity theory (last accessed 20 Dec 2012) http://www.bath.ac.uk/research/liw/resources/Models%20and%20principles%20of%20Activity%20Theory.pdf
Engeström.Y (2008) From Teams to Knots: Activity-theoretical studies of Collaboration and Learning at Work. Learning in doing: Social, Cognitive & Computational Perspectives. Cambridge University Press. Series Editor Emeritus. John Seely Brown.
Engeström.Y (2011) Learning by expanding: ten years after (last accessed 19 Dec 20-12) http://lchc.ucsd.edu/mca/Paper/Engestrom/expanding/intro.htm
REFERENCE
Ackoff, R.L. (1979) The Art of Problem-Solving, New York: Wiley
Conole, G (2011) Designing for learning in a digital world. Last accessed 18 Dec 2012 http://www.slideshare.net/grainne/conole-keynote-icdesept28
Conole, G. and Oliver, M. (eds) 2007 Contemporary Perspectives on E-learning Research, Themes, Tensions and Impacts on Research. London, RoutledgeFalmer.
Cussins, A. (1992). Content, embodiment and objectivity: The theory of cognitive trails. Mind, 101, 651–688.
Engestrom (2008-04-30). From Teams to Knots (Learning in Doing: Social, Cognitive and Computational Perspectives) (p. 238). Cambridge University Press. Kindle Edition.
Engeström, Y. (1987) Learning by Expanding: An Activity-theoretical Approach to Developmental Research. Helsinki: Orienta-Konsultit.
Engeström, Y. (1994). The working health center project: Materializing zones of proximal
development in a network of organizational learning. In T. Kauppinen & M. Lahtonen (Eds.) Action research in Finland. Helsinki: Ministry of Labour.
Engeström.Y (1999) Learning by expanding. Ten Years After. http://lchc.ucsd.edu/mca/Paper/Engestrom/expanding/intro.htm
Engeström.Y (2008) From Teams to Knots: Activity-theoretical studies of Collaboration and Learning at Work. Learning in doing: Social, Cognitive & Computational Perspectives. Cambridge University Press. Series Editor Emeritus. John Seely Brown.
Griggs, R.E. (1985) 'A Storm of Ideas', reported in Training, 22, 66 (November)
Issroff, K. and Scanlon, E. (2002) Using technology in higher education: an Activity Theory perspective. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 18, 1, 77–83
Knorr-Cetina, K. (2003). From pipes to scopes: The flow architecture of financial markets. Distinktion, 7, 7–23.
Kuutti, K. (1996) Activity theory as a potential framework for human–computer interaction research. In B. Nardi (ed.) Context and Consciousness: Activity Theory and Human–Computer Interaction. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, pp. 17–44.
Leon’tev.A.N. (1978) Activity, consciousness, and personality. Englewood Cliffs. NJ. Prentice-Hall.
Moessenger, S (2011) Sylvia’s Study Blog (Last accessed 19 Dec 2012) http://sylviamoessinger.wordpress.com/2011/02/26/h809-reading-oliver-et-al-chapter-2-a3-6/
Phipps, L., Witt, N. and Kelly, B. (2005) Towards a pragmatic framework for accessible e-learning. Ariadne, 44. Online. Available HTTP: <http://www.ariadne.ac.uk/ issue44/ phipps/> (last accessed 19 Dec 2012).
Rheingold, H. (2002). Smart mobs: The next social revolution. Cambridge, MA: Perseus.
Ritchey, T. (2011) Wicked Problems - Social Messes: Decision support Modelling with Morphological Analysis.Springer.
Rittel.W.J., Webber.M.M. (1973) Dilemmas in a general theory of planning Policy Sciences, June 1973, Volume 4, Issue 1,
Seale, J. (2006) E-learning and Disability in Higher Education: Accessibility Research and Practice
VanGundy, A.B. (1988) Techniques of Structured Problem Solving, 2nd ed, Van Norstrand Reinhold. Techniques 4.01, 4.06, 4.57
Vygotsky.L.S. (1978) Mind in Society. The development of higher psychological process. Cambridge. MA.
Wikipedia (2012) Definition of 'Historicity' - (last accessed 19 Dec 2012) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historicity
Zerubavel, E. (1997). Social mindscapes: An invitation to cognitive sociology. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.