A pedagogy of abundance explains a good deal and changes everything
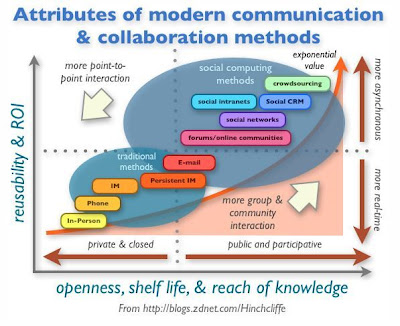
From Dion Hinchcliffe
A pedagogy of abundance
This forms a chapter in Martin Well's new book.
If you are studying the Masters in Open and Distance Education MAODE (any module) with The OU you need to read this.
Weller takes us through a series of clearly expressed, persuasive steps, a brief history about the more recent shifts in education and how Web 2.0 changes everything.
I conclude that the nature of learning is reverting to its natural, un-institutionalised and a pre-formal classroom based model, whereby you learn on the fly vicariously, turning to groups and individuals of your own choosing, exploiting the abundance of the web to inform and connect, an apprentice of anything, perhaps even at times with a tutor or fellow students, in an experience that is more akin to that of a governess to child, or tutor to older student or expert and scholar.
Boyer (1990) established what scholars do
1) Discovery
2) Integration
3) Application
4) Teaching
It intrigues me that this set of activities or practices is precisely what one does in social media:
1) Seeking out through research those 'spheres of influence' where the discussions are generating something fresh and pertinent, that is informed, even scholarly and that you proactively integrate this 'sphere of influence' which might be an individual (blog, podcast, video) or a social media platform group, into your own online 'realm of thinking' through bookmarks, joining a group (and engaging in its vortex).
2) Engaging tentatively in some forums.
3) From observation on the periphery (Seely-Brown) to growing levels of participation you gain the confidence to apply what you understand to the degree that you too in turn not only express your thoughts in blogs, forums and discussion groups, but
4) find yourself teaching others, itself a learning experience. Weller implies that to understand what could happen in education we ought to consider the shift in the way in which we purchase digital artifacts compared to the physical object, that just as the abundance of music, movies and books in digital form has altered our behaviours regarding shops and shopping, so the ready availability of digitised learning materials is inevitably altering the way students view and purchase education.
We are moving from a model based on the economics of scarcity to an economics of abundance.
Here, though Weller doesn't offer it, a brief consideration of how centres of learning formed in the distant past is of value. How students gathered around a scholar, then as the technology made possible, books containing information and scholarly thought were gathered into collections.
The student and educators had to be physically present and thus our university towns were formed.
The formation of and subsequent success of establishments such as the Open University (begun 42 years ago) shows that separation of student and campus was possible where the technology and logistics meant that through books, TV, radio, tapes, and subsequently DVDs and the Internet the learning experience could be divorced from the campus. This dependence on the physical artifact is now dissolving too, the expense is no longer represented in the book, indeed the idea of a collection of many chapters in one place is challenged as the Internet allows far greater tailoring of content to the learning object.
Is this not a return to a more natural way of doing things?
Should we be turning for input here from to the social anthropologist and educational psychologist here?
Have we ever learnt in units of engagement that endure through the entire contents of a book in one sitting?
I wonder if the cook book as a model for e-learning is an apt one?
Chris Anderson (2008)
The future modus operandi might be to give away '90% of a product to earn 1 %'. The logic of accepting the way in which digital stuff is created, marketed and sold implies that the 'long tail of higher education' (let's keep kids at school for now), will give much more control to the student purchasing their education; that niche and tailored learning will be desired.
Of far greater worry, unless you and your institution are readily able to embrace change as an early adopter, is that modules themselves, like a set of wikipaedia pages offered in a myriad of personalised sequences, can be assembled like a set of smart Lego bricks by the learner themselves making substantial parts of an institution's functions redundant. Indeed, being able to slot in up-to-date content, easily achieved beyond the confines of a module, is indicative of a weakening in the relationship between institution and student.
There is less dependence on specific course materials when most references can be sourced with ease.
Even the social aspect of the campus based education is challenged
Think of it as a form of tourism, education as an opportunity to socialise, be entertained and to entertain, then this can be done online. (Don't we all go to university as undergraduates for the 'crack'?)
The gap between the physical and the virtual experience has closed
Can learning be purchased, consumed and certified like an eBook from Amazon?
Should the Milton Keynes Campus of the Open University be taking greater head of the vast distribution warehouses of Amazon on the other side of the M1?
Do you need the expert if their insights can be purchased through various forms of asynchronous communication? (a book) Or their synchronous insights and expertise supported by the hour through a webinar or Skype-enabled tutorial? If the sphere of influence is reduced to that of professor and scholar, as that between a piano teacher and pianist do we need the institution at all?
And in a world where all qualifications are not the same even if they have the same name, is the only outcome that matters for the individual, their job and how they consequently perform (or if it is an MBA how their business performs)?
If the same learning outcomes are offered, using largely the same set of materials in a sequence that is logical and engaging and will in any case be far more challenged or enabled by the context in which the student is learning, then surely the deciding factor is price and the only way to decide on which price to pay has to be a combination of the depths of your pockets and the perceived and actual desirability of the brand.
If Harvard Business School, for example, as the Mercedes of business schools, can now offer, like the car manufacturer, a range of products to suit different pockets, all with the same brand values and distributed with ease over the Internet, then how do others compete?
Or what if its star product, once limited by the physical limitations of a campus and the manageability of a cohort can be purchased by thousands?
Perhaps in a growing market, with significant demand, space remains for many players and new players. However, as any Internet search shows, if you are learning online the deciding point, exactly as a purchase of a packet of Cornflakes, comes as you reach up to the shelf and select product B rather than product A.
Might it be, that having been the only product for several decades, the Open University's 'product A' is competing with a rich alphabet of alternatives, many written and supported without doubt if you look at the lists of academics and personal by people who were originally taught by or taught at The OU.
If the model is to give away the digital object and make money on the physical then Oxbridge, Ivy League and other campus based institutions could potentially increase their intake 12 fold by running all courses online, with physical presence limited to three one week long residential sessions.
The College turns into a B&B with the residents changing every week, rather like the turn around days you have at a resort.
At no stage is contact with fellow students, tutors or the college itself ever diminished, as everyone is readily contactable thanks to a smartphone and a laptop. Likewise distance learning Institutions such as The OU to compete with these upstarts should offer a campus based experience by creating permanent bases strategically all over the world.
If we think of education as music, then we have two forms, the folk form inexpensively delivered in homes and community spaces and the elite form of the expert or most popular performer in access-restricted palaces and assembly halls. Whilst historically we have seen the music industry of the last century as the democratisation music, in hindsight, with the Internet, even this looks like a restrictive practice, holding purchasers back by the schedule of production, distribution and sales. Books are going the same way as CDs; as both are formats for learning materials, is it not simply the case that with lectures, tutorials and assessment online, that there is an expectation from all quarters that we can have it all, anywhere, any time? And that this can be achieved by any institution. It isn't difficult to digitise content, you simply don't go to print. Brand, like purchasing Cornflakes, the price and what you can afford is the only differentiator.

An activist model.
While access to expertise remains rare, we have access to journals, videos, blogs, podcasts, slidecasts, also discussion forums, comments, and blogs. Weller (2011)
And these experts, certainly in distance learning institutions, are often bound only, like the students, by lengthy threads to remote locations. Their reputation, the weight of their knowledge a product of those parts of their thinking that has been published for public consumption. It then comes down to the quality of learning experience through tutors, online and other support. We should think of each online module as a virtual game, with all those ins and outs and possibilities thoroughly tested for the experience; exactly, in fact, as occurs in the Institute of Educational Technology at The OU.
Siemens (2005) considers the shift to greater control by the learner rather than the institution.
Constructivism, social constructivism and now connectivism are the learning paradigms. If education at close quarters in the Oxbrdige tutorial, involves dialogue, reflection and critical analysis, these are the same qualities that can be achieved online at less cost and at greater convenience.
The essence of learning
Conole (2008) Web 2.0 the collective and the network.
As in the physical world with its cliques and networks, from old school-tie to Free Masons, so online, despite our desire to exploit the ability to connect, there are controls and limits. You cannot wade in and exchange with much authority, the hero expert author of the books or papers yiu have come to admire. Seely-Brown and others are right to consider how all of us, unwittingly or deliberately, first engage as an apprentice of some sort. We must begin on the periphery. If dropped into the heart of things too soon our ignorance will mean we have no purchase at the centre and centrifugal forces will cast us aside.
As one commentator is right to point out, the Internet is the real world. A movie, or novel is fiction, but online with increasing ease, we behave in just the same way with someone a thousand miles away as someone sitting opposite us.
Web 2.0 = niche communities, social purposes, collective political action, amateur journalism, social commentary.
Just as we can have the successful, recognised and respected amateur journalist and amateur sports coach, so surely can we have the amateur academic, if only in the sense that none of these people are paid. We can all surely think of professional journalists, coaches and academics who are amateurish in their words, actions and thoughts. Just as there are successful 'citizen journalists' even the 'amateur novelist' who self-publish are there not likely to be 'amateur scholars' even tutors, anyone with that vocational desire to share their thinking in order to develop the knowledge of others?
Have we not reached a stage with the plethora of quality content online and the multitude of groups that you could join, that you could learn a great deal to a high academic standard or level of performance, entirely for free both in cost terms and the constructs of an educational institution. You may not have the piece of paper at the end of it or the letters after your name, or indeed the title before your name, but when did any qualification qualify you to do something with it?

Seely-Brown and Adler (2008) talk of this shift to participation and demand-pull.
They talk of education being:
- Free
- Abundant
- Varied
- Easy
- Socially based Connections light
Shirky (2008) Organisations
User generated content
In a world of abundance the emphasis is less on the creation of new learning materials than on the selection, aggregation and interpretation of existing materials. We don't need more, we need systems that let us draw in the freshest and most significant content on the fly. Dare I also suggest that just as music is easily copied and shared for free, that course content, and the learning design can just as easily be lifted and reconstituted? Weller 2011 i.e. New learning content becomes the remit of students who through the abundance of stuff and connectivity generate new content. The trick is to isolate those places where people of a like-minds gather. You cannot join more than a handful of groups and take part and so contribute or gain anything. The tasks therefore becomes to find or form such groups.
Barrows and Tamblyn (1980) problem based learning. Is identified as the old way of learning.
That you present a problem then teach a way to solve it.
Wenger (1998) the social role of learning and apprenticeship as 'legitimate peripheral learning'
Bacon and Dillon (2006) Communities of practice.
Siemens and connectivism.
The real issue is user-based content. Eric Schmidt, CEO Google. More content is generated and put online in any two days in 2011 than was created, published or broadcast between the development of the first means of mass distribution, the printing press and the coming of the Internet. We do in our millions, with extraordinary ease, in 48 hours what had taken some 600 years to do.
REFERENCE
Weller, M. (2011) in Spanish Journal of Pedagogy, 249 pp223-236