 |
| From E-Learning IV |
Fig 1. Essential reading on British Forces on the Ypres Salient in 1917
I take back what I said a couple of days ago about a module (not OU) that comprises a reading list and set of essay questions. Sometimes I feel the OU modules I have done are too prescriptive, that all of us are passengers on a learning train that will not permit anyone to leave the service. You work from and are assessed on the content given - excellent, succinct and contained. This does not suit everyone; never does the scary freedom to read from a reading list. In many cases the variety seen in both approaches, with overlap, is how and when one comes to understand something.
Back to formal reading
It matters that you are directed to the right book. This is the right book on Passchendaele to understand from a general strategic, to operational, to tactical level what took place.
I read 'Passchendaele: the untold story' first in May for a presentation in June.
The purpose was to lay out the chronology of events and compare two battles within the Passchendaele or 'Third Ypres' conflict relating to command. I took notes: highlighted in the eBook which I then typed up in a Google Doc before creating a presentation. Over two months later I read the book again as if I had never seen the book before; on the one hand I worry about my sieve like brain, on the other I am intrigued to understand what is going on.
 |
| From E-Learning IV |
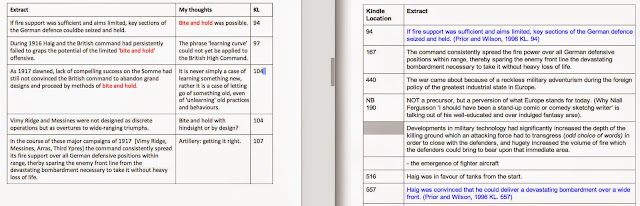
Fig.2 Notes taken in Google Docs from the highlight sections in the eBook
On second reading, with the tracks and sleepers of the general chronology becoming established and retained knowledge, and with an essay title ringing in my head, the highlights I make in the eBook are, with a few exceptions, totally different. I am reading the same book, but taking something very different from it. I have a highly selective, easily distracted brain - nothing sticks if it doesn't have to. I know a few people with a photographic memory: they appear to read something once then have the entire contents at their fingertips to apply to a problem. My memory is the opposite - nothing at all that I don't deem of importance to the task at hand will be retained. I have, side by side, the notes I took in May and the notes I am currently taking - they could be from different publications; I struggle to find any common ground.
There will be a third reading
This third reading will have different purpose as in due course I write a comparative history between Third Ypres: Passchendaele and the First Gulf War to fulfil a desire to respond to something my late grandfather said in 1992 'That's nothing compared to Passchendaele' he said as he watched the First Gulf War unfold on TV. He saw the differences between foot soldiers as unrecognisably different, whereas I saw the prospect of having a leg blown off or being gassed as more than faintly similar. Had the generals used the tactics of 1992 in 1917 they would have gained more ground and lost fewer men; something had been learnt in 75 years of war then.
Fig.3. The mud of the First Gulf War
Visualising the above I imagine a desert; the state of my brain before I read, that over time acquires an invasion of cacti, followed by ground cover plants, until eventually there are established trees and a rich ecosystem.
Hardly surprising, but on second reading you pick out more detail; you see things that you missed, or couldn't take in the first time round. I'm the kind of person who would apply this to entire modules: that the student who wants to should be allowed to, for a considerable discount, to re-sit a module they have already done. Why not even a third time if your goal is to master a subject? A' Level students with poor grades will 'cram' for a year to improve on these. Through-out life things we want to do are achieved as a result of tackling the problem repeatedly until we crack it.
Finally, I conclude, that given how complex we are, so learning needs to offer a similar level of variety; there can be no perfect system, or learning design pattern. We learn in different ways, and educators teach in different ways. E-learning isn't a panacea, it is simply another approach the complements ones we have always adopted, not least learning directly from experts themselves through talking things through.
More of us should be able to or should have been able to retake classes we flunked - with a different teacher, if not in a different institution. It shocks me to see how a student at school can be put off a subject they enjoy as they don't relate to or get on with the teacher - so change the teacher.
