Read this web page and consider to what extent the six challenges mentioned are addressed in your context:
Mis-Adventures in Alt Format (Stewart, 2007)
http://www.altformat.org/index.asp?id=119&pid=222&ipname=GB
Pick one challenge and write a paragraph in your tutor group wiki explaining how it is relevant to your context.
____________
Developing a total picture of how Alt Format fits into the broader discussion of curricular reform and modernization will help insure that we do not continue to live on the margins of the educational mainstream. (Stewart, 2007)
'Universal Design for Learning'
Challenges in relation to Alternative Formats:
- How does the provision of Alt Format fit into other emerging models for data management and delivery?
- How do we build systemic capacity to meet the projected needs for Alt Format and Accessible Curricular Materials?
- How do we align the divergent Alt Format efforts occurring on an international bases so that they minimize redundancies and duplicative efforts?
- How do we move beyond the current focus on Blind and Visual disabilities to a more holistic model of access for the gamut of print disabilities?
- How do we develop the level of technological literacy in students with print disabilities that will be necessary for them to benefit from the technological evolutions that are occurring in curricular access?
- How do we involve all of the curricular decision makers in the process of providing fully accessible materials?
In my context
1) How does the provision of Alt Format fit into other emerging models for data management and delivery?
With the digitization of everything a further step to ensure content is also accessible should be taken at the time of conversation or creation. I’m not aware in an agency where this ever occurs and when there is a client request the response is a simple one - word or PDF formats, or look to the browser of platform where the content will sti.
2) How do we build systemic capacity to meet the projected needs for Alt Format and Accessible Curricular Materials?
Is there a more appropriate agent to handle the conversion and delivery of electronic content on a given campus or system of campuses? I’d probably consider the Open University itself, or the Business School where I worked for a while. I know the disability officer, but his role was more to do with access and personnel and visitors to the building then meeting student needs - which I presume comes under Student Services.
3) How do we align the divergent Alt Format efforts occurring on an international bases so that they minimize redundancies and duplicative efforts?
Whilst efforts can and have to be made to improve access universally might the fine detail be left to address either group issues by working with representatitives of associations for, for example, the blind, dyslexia, cerebral palsy and other groups ? Learning from then improving such practices and tackling access for people from these groups for specific subjects and specific levels on a strategic basis knowing that complete coverage is the goal?
‘A plan for the development and incorporation of emerging technologies in a holistic and self-sustaining model is incumbent. These emerging systems must be based on flexibility and economies of scale if we are ever going to get in front of the issues of materials access.’ (Stewart, 2007)
4) How do we move beyond the current focus on Blind and Visual disabilities to a more holistic model of access for the gamut of print disabilities?
Doesn’t cover everyone who would benefit and would benefit other groups, such as non-native language populations, remedial groups and as an alternative for any user who may prefer or benefit from the text record.
5) How do we develop the level of technological literacy in students with print disabilities that will be necessary for them to benefit from the technological evolutions that are occurring in curricular access?
In many anecdotal reports, less than 10% of the incoming students to higher education have ever had any realistic exposure to the access technologies they will need to be successful in adult education and in the world of work. (Stewart, 2007)
Current studies suggest the opposite, that students with disabilities who gain so much from having a computer to access resources, that they are digitally literate. There are always people who for all kinds of reasons have had less exposure to or are less familiar with the technology -whether or not they also have a disability.
6) How do we involve all of the curricular decision makers in the process of providing fully accessible materials?
The original authors never have a say or make a contribution to the reversioning of content for use by disabled students.
This method of access often times results in the retrofit of existing materials, or the creation of alternative access methods that are not as efficient or well received in the general classroom environment. (Stewart, 2007)
For a truly effective model to be developed the original curriculum decisions should be made in a context of understanding the needs of all learners, and in particular those learners who do now have visual orientation to the teaching and learning process. (Stewart, 2007)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interview analysis revealed five personal factors that appeared to influence students’ decisions about technology use:
- a desire to keep things simple,
- a lack of DSA awareness,
- self-reliance,
- IT skills and digital literacy,
- a reluctance to make a fuss.
The three most talked about factors were desire to keep things simple, IT skills and digital literacy. Seal and Draffan (2010:455)
‘The are many ways of making and communicating meaning in the world today.’ Conole (2007:169)
The kind of problems students with disabilities now face are different - less whether content has been made available in a digital format, but how good the tools and services are to access this content.
- accessibility of websites and course/learning management systems (CMS)
- accessibility of digital audio and video
- inflexible time limits built into online exams
- PowerPoint/data projection during lectures
- course materials in PDF
- lack of needed adaptive technologies.
Students also mentioned technical difficulties using e-learning and connecting to websites and CMS, problems downloading and opening files, web pages that would not load, video clips taking too long to download, poor use of e-learning by professors and their own lack of knowledge working with elearning.
For most groups of students, solving e-learning problems by using non e-learning solutions was also popular.
During the last decade there has been tremendous development and interest in e-learning on campus. While our research shows the many benefits of e-learning, such as the availability of online course notes, there are also problems. Chief among these are problems related to inaccessibility of websites and course management systems. (Fitchen et al 2009:253)
Digital Agility
Results suggest that an important personal resource that disabled students in the study drew on when using technologies to support their studies was their ‘digital agility’. Seal and Draffan (2010:449)
Use of assistive technologies
Many students with disabilities have, since 2007, developed strategies for the use of both specialist assistive technologies (e.g. IrisPro, quill mouse, Kurzweil, Inspiration or Dragon Dictate) as well as more generic technologies (e.g. mobile phone, DS40 digital recorder, Google) Seal and Draffan (2010:450)
Seal and Draffan (2010:451) therefore suggest that disabled students have the kind of ‘sophisticated awareness’ that Creanor et al. (2006) described when they talked about effective learners being prepared to adapt activities, environments and technologies to suit their own circumstances. This contradicts somewhat the arguments of Stewart who argues that disabled students are behind other students in terms of developing digital literacies.
The digital agility of the students, identified in the study, is significant in terms of encouraging practitioners not to view all disabled students as helpless victims of exclusion. Digital inclusion does not always have to be understood through the dual lenses of deficits and barriers. Seal and Draffan (2010:458)
REFERENCE
Conole, G and Oliver, M (eds) 2007. Contemporary perspectives in E-Learning Research. Themes, methods and impact on practice.
Fichten, C. S., Ferraro, V., Asuncion, J. V., Chwojka, C., Barile, M., Nguyen, M. N., & ... Wolforth, J. (2009). Disabilities and e-Learning Problems and Solutions: An Exploratory Study. Journal Of Educational Technology & Society, 12(4), 241-256.
Seale,J., Draffan,E.A. (2010) Digital agility and digital decision-making: conceptualising digital inclusion in the context of disabled learners in higer education, Studies in Higher Education, 35:4, 445-461
Stewart, R (2007) Mis-Adventures in Alt Format
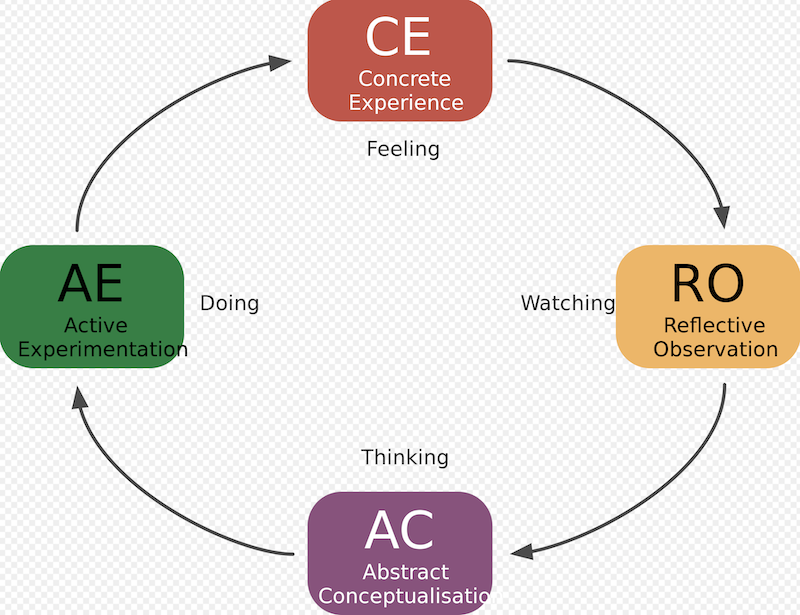

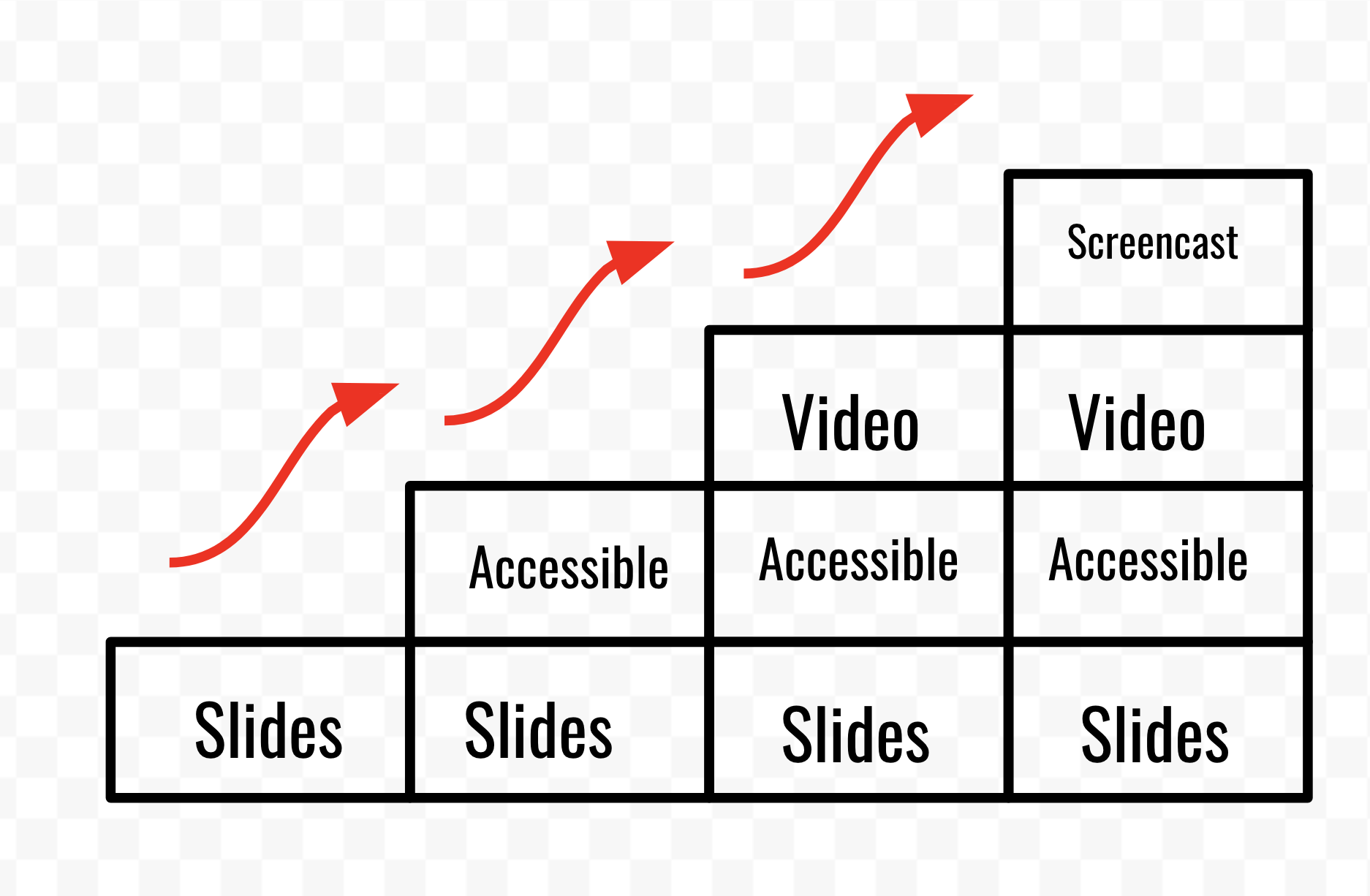

 Activity Three I want to replace with my own video so from the outset the message is for students rather than me saying that they should hear 'student' every time the presenter says 'Teacher'. Also to diminish the negativity on some slide presentation types than might be overly reliant on the slides and the handouts rather than students taking notes. Taking notes is a totally foreign concept, not even students who may benefit from recording audio or video so they have something to play back. I nabbed this LINK > https://youtu.be/GuA8fPCHu9c from Open Learn's Take Your Teaching Online'.
Activity Three I want to replace with my own video so from the outset the message is for students rather than me saying that they should hear 'student' every time the presenter says 'Teacher'. Also to diminish the negativity on some slide presentation types than might be overly reliant on the slides and the handouts rather than students taking notes. Taking notes is a totally foreign concept, not even students who may benefit from recording audio or video so they have something to play back. I nabbed this LINK > https://youtu.be/GuA8fPCHu9c from Open Learn's Take Your Teaching Online'.