Another fantastic opportunity to use my SCONUL access rights and explore the archives at the University of York.
The Rare Books collection holds on long-term loan all those pre-1800 books that were part of the library of the Community of the Resurrection at Mirfield, West Yorkshire. This Anglican religious community for men was founded in Oxford in 1892, and moved to Mirfield in 1898. The library was built up mainly by gifts from members and friends, and contains much valuable early material - including this copy of......
Auslegung der Episteln und Evangelien von Advent au bis auff Ostern, written by Martin Luther and published in the town of Magdeburg in 1533.
It has been absolutely fascinating, and also just an amazing privilege, to examine this nearly 500 year old book - a real primary source from the heart of the Lutheran Reformation!
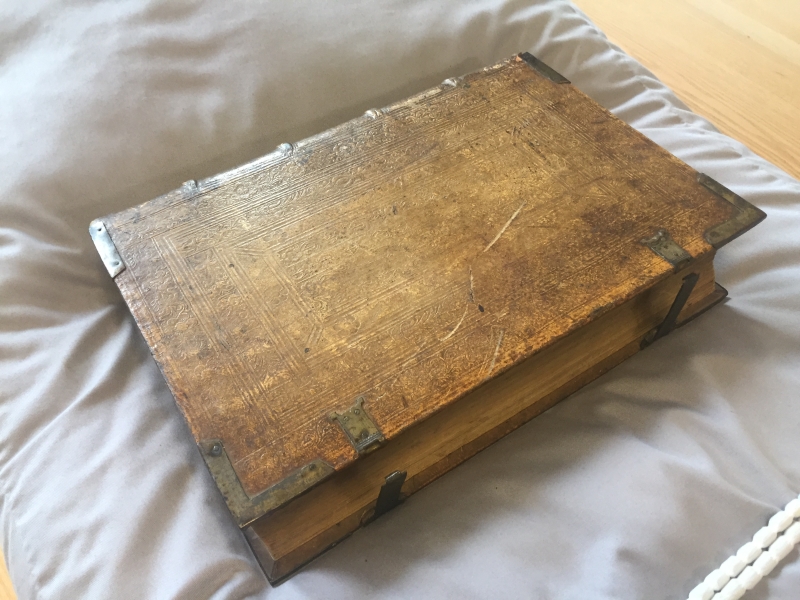


The book is a postil, a collection of sermons by Martin Luther on each of the prescribed weekly Bible readings from the Gospels and the Epistles in the period from Advent to Easter. Further collections were made of Luther's interpretations of the readings for the rest of the year - eventually collected into what become known as his Church Postil. The term postil is derived from the Latin post illa verba textus ("after these words from Scripture")
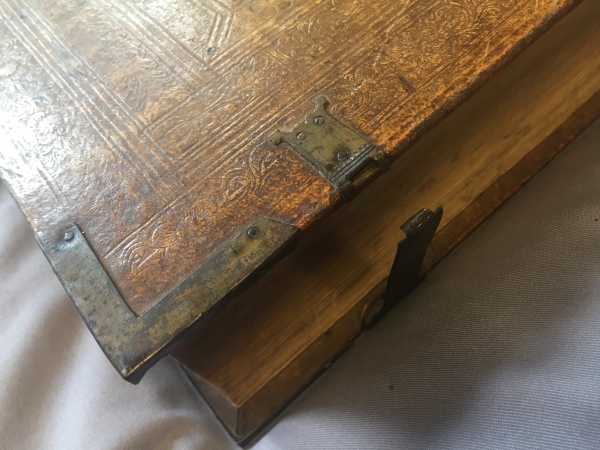
It is a hefty tome, bound in leather - I think it is just 'blind tooled', although perhaps there is some gilt remaining in places. The covers are wooden and there are metal corners and two clasps. There is a little damage by wood worm, both to the covers and some gently nibbled pages.
It was once the property of someone called 'Hans Voyt', who has added his name to the ornate title page - which also highlights that the text has been corrected by Martin Luther and contains a 'new register' (essentially an index) - I'm guessing the ability to have a standard page length and numbering in every copy made indexing so much more straightforward in printed books - a 'new feature'.


There are lots of points to note on the page layouts and the different printed features in the book. I assume that there was a combination of metal movable type and woodblocks for the decorated capitals and illustrations. There was a side margin printed that summarised key aspects of the sermon text and woodblock pictures were spread throughout the pages. I wonder what the presence of these illustrations tells us about the intended readership - were these pictures 'entertainment', symbols of the added value embodied in a high end gift, did they have an educational objective in addition to supporting the text, was this just 'the fashion'?



I haven't found any reference anywhere yet to a specific illustrator, but I did find a small monograph in just one of the pictures shown below (John the Baptist is in prison on the left and checking out whether Jesus is 'he that should come?') I think it's probably 'HB'. There is a famous artist, Hans Brosamer, who I've found illustrated a number of publications at that time - but his 'HB' monograph looks different with the H run into B not distinct as in these letters. Something to look into further if I get the chance - but I guess most illustrators went unidentified if they weren't themselves a 'name' that might help sell the publication.


I liked the bit of 16thC cosmology shown below, with sun and moon rotating around the newly formed world - and Jesus sliding down to earth from the mouth of (a very Papal-looking!) God. (I'm struggling with the lettering that circles the world - is it perhaps 'God's Word'?)

Some great anachronistic knights accompany the three kings on Epiphany - and presumably the agents of King Herod on the way to do no good in the background (the stable has scrubbed up well too 😃)

The end of the postil confirms the printer to have been Michael Lotther. The Lott(h)ers were a multi-generational family of printers closely linked to Martin Luther and the Reformation. Luther had supported Melchior Lotther the Elder to set up as a printer in Wittenberg, and his sons Melchior (the younger) and Michael both entered the trade. Michael had moved out of Wittenberg to set up shop in Magdeburg by the time this work was being printed in 1533 - he remained close to Luther though and married into his family.

However, the book doesn't end there. In fact there is a second printed work bound together with it - another Reformation text, produced at the same time - but by a different printer and in a different city altogether.
Kirchen Ordnung. In meiner gnedigen herrn der Marggraven zu Brandenburg und eins erbern Rats der Stat Nürmberg Oberkeyt und gepieten, wie man sich bayde mit der leer und Ceremonien halten solle
These are Kirchen Ordnung, Church Orders - basically an agreed set of new 'rules' that a Lutheran church community should follow now that the old Catholic 'ordnung' had been set aside. I think in the early years of the Reformation there were a number of different regional/local formulations of church regulations, these are the set created by the Margraves of Brandenburg and the imperial city of Nuremberg.
They were printed in the city of Nuremberg in 1533 by the Gutknecht press and they helped to produce more uniform and stable approaches to worship amongst Lutheran churches both in that area and across Europe.

Whilst this part of the book has none of the fine illustration of the postil it does have quite a lot of two colour printing (I assume this was two impressions through the press) - most of this is in the description of the liturgy to distinguish the words of priest and congregation. There were also four pages of musical notation - I eventually worked out that this is plainsong to accompany the mass, 'Our Lord Jesus on the night he was betrayed...'
These are 'neumes', a way to denote choral chants before the five line staves and notes we are now used to. This style is a specifically German form - 'Gothic neumes' or Hufnagel - 'Horsenails' as they looked like the nails used to shoe horses.
I'll have to see if I can make musical sense of it - so far I have even't worked out what the clef means!

Given that this book is made up two separately printed texts I'm left with lots of questions about how and when these were brought together. Whilst there is a discontinuity in the printing style and the page numbering the appearance of the pages looks to have similar wear, the edges look to be discoloured to the same extent. I couldn't distinguish two 'sections' from the 'outside', so perhaps there is evidence that they have been bound together for a long time. Both texts are probably 'working documents', I can imagine how each would be of value to a Lutheran cleric - biblical exegesis and practical summaries of the new Reformed regulations and liturgy - a useful combination within one book.
One further observation might be of relevance to dating the book. Both the front and back endpapers have a faint watermark. I spent a long time trying to make it out and subsequently discovering a whole world of scholarship based around collecting and cataloguing paper watermarks. The mark is of an ox's head, with a letter 'M' below its mouth and a cross and entwined snake above. The best match I could find (and I think it is pretty much on the money) is a mark which is recorded in 'Briquet Online' having been recorded in a Copybook in Prague in 1534.
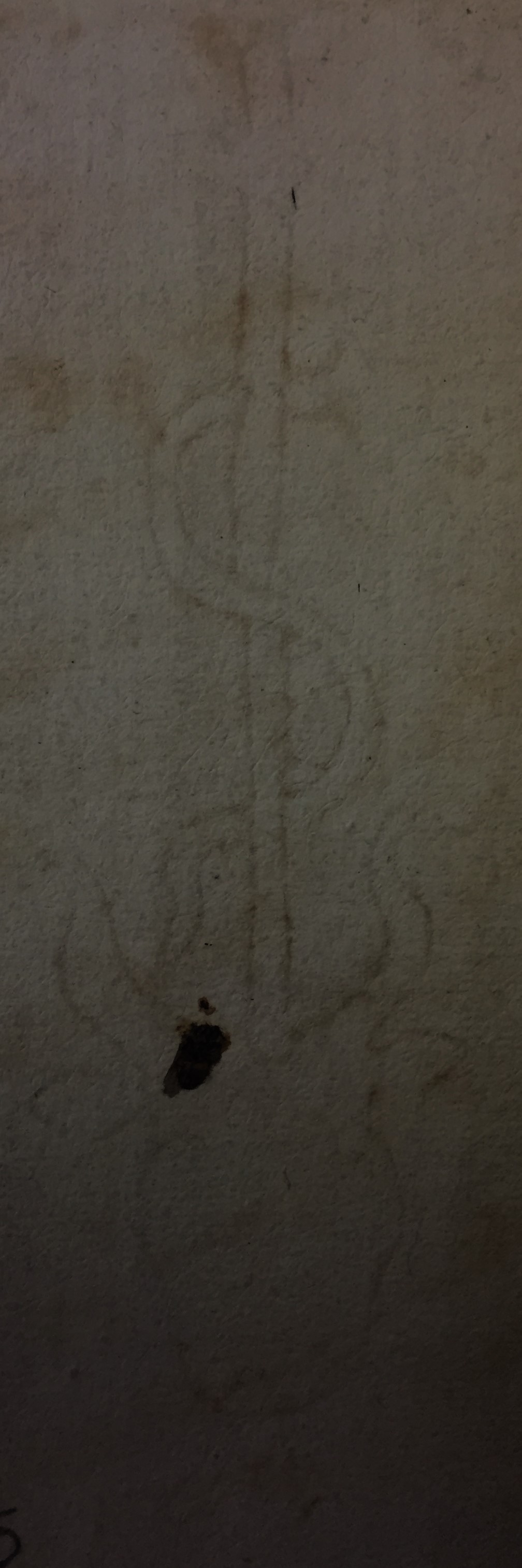

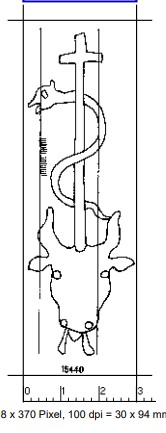
So, on the basis of the watermarks there is some evidence that the two seperate texts may have been bound together not that long after they were originally printed. The information I've found so far about paper watermarks is clear that you have to be very cautious in assuming similarity means that you can 'date' or 'locate' documents - but I think there's at least some basis for arguing that the current book may have been created sometime in the 1530's.
I've been astounded how many different strands of the A113 content came together in just this single artifact: technical aspects of printing (woodblocks/type/colour); printing and music (and the history of musical notation); the role of Martin Luther in 'expert' interpretation of God's word - not something that everyone in the 'priesthood of believers' could be trusted to do; the use of the German vernacular throughout; the challenge of bringing new regulation to control the revolutionary diversity of the new beliefs.
Examining this object was a really valuable experience and one I hope to come back to - perhaps to think more formally about a 'source analysis'.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bibliography
Primary source:
Luther, M. (1533). Auslegung der Episteln und Evangelien von Advent an bis auff Ostern; anderweit corrigirt durch Martinum Luther, etc. Wittenberg: Michael Lotther. [From an original held at the Borthwick Institute for Archives, University of York (https://www.york.ac.uk/borthwick/)]
To help identify the original documents:
Kirchen Ordnung. In meiner gnedigen herrn der Marggraven zu Brandenburg und eins erbern Rats der Stat Nürmberg Oberkeyt und gepieten, wie man sich bayde mit der leer und Ceremonien halten solle Nürmberg: Gutknecht,1533 [via the digitisation portal of Rhineland-Palatinate dilibri]
Auslegung der Episteln und Evangelien von Advent an bis auff Ostern; anderweit corrigirt durch Martinum Luther [via the Deutsche Digitale Bibliothek]
To help identify the paper watermarks:
Briquet Online (v. 2.1 - 2021-01-23)
Background on the Lotthers:
Reformation Printers: Unsung Heroes
Author(s): Richard G. Cole
Source: The Sixteenth Century Journal , Autumn, 1984, Vol. 15, No. 3 (Autumn, 1984),
pp. 327-339
Published by: Sixteenth Century Journal
Stable URL: http://www.jstor.com/stable/2540767
Tillmanns, W. G. (1951) "The Lotthers: Forgotten Printers of the Reformation," Concordia Theological
Monthly: Vol. 22, Article 23.
Available at: https://scholar.csl.edu/ctm/vol22/iss1/23