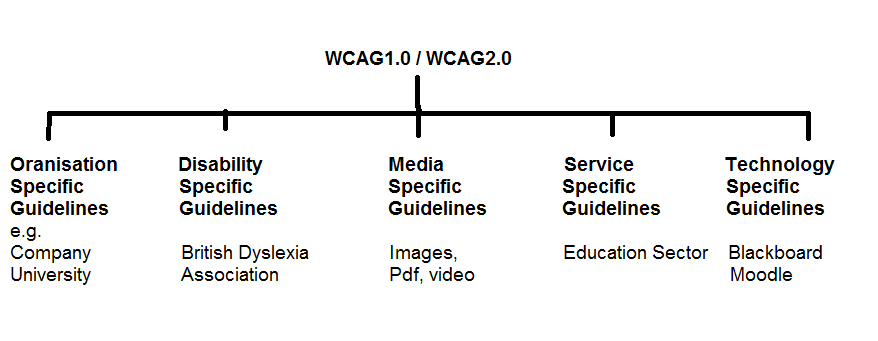
H810: Week 16: Activity 35.1: Seale Chapter 12
Seale identifies six potential areas for conflict or contradiction within an organisation or activity system. What potential contradictions exist in your organisation and why?
I have had problems with this chapter at first as H800 introduced me to third generation activity theory which examines contradictions between systems rather than examining contradictions within one system as in the second generation activity theory described by Seale in chapter 12. For example, In H800 I looked at how Engeström's (2001) third generation activity theory could apply to the Geology department at Keele University with whom I work closely. The reduction in government funding to universities and the need for increased diversity has led to the development of modules delivered completely on-line. I drew the following diagram where two interacting systems produce contradictions which Engeström (2001:137) predicts are the 'sources of change and development'.
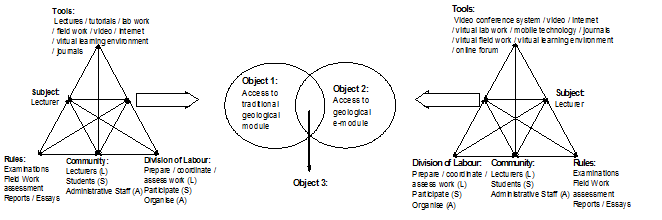
I found it useful as a starting point to identify where the contradictions lie and then to proceed to examine them before I went on to design an e-learning module.
I believe that third generation activity theory would be a useful technique to look at institutional response to accessibility (chap 11) but the way Seale has used second generation theory in chapter 12 concerns me as activity theory is designed to illustrate a situated activity and looking at interactions between just two aspects of the activity results in the study of isolated concepts and reduces the effectiveness of a holistic image.
Subject: lecturer
Tools: guidelines, evaluation and repair tools
Rules: institutional and departmental policies and strategies
Community: students, lecturers, technologists, support services developers, managers etc.
Division of labour: planning and funding, designing and developing, implementing and evaluating, using, supporting, advocating
Object: to make e-learning accessible
- Contradiction between the object and the tools
Confusion over guidelines - which ones to use
lack of training / guidance on tools - Contradiction between the object and division of labour
Always someone else's job - affected by workload and belief in complexity of the task.
For example, rules might dictate that accessible learning activities are designed by technicians who have no idea how to adapt materials to achieve the learning objectives. - Contradiction between the community and the division of labour
'Who does what' arguments similar to above. For example, departments may have different ideas on who has the responsibility to produce accessible learning materials. - Contradiction between the community and the rules
Often the institutional rules and departmental rules conflict. Universities have so much infighting between departments that it makes it difficult to get co-operation and accessibility issues need co-operation! - Contradiction between the rules and the subject
Lecturers having weak or inconsistent guidelines - Contradiction between the tools and the subject
Lecturers having difficulties using tools
According to Searle, "any or all of the contradictions will prevent accessible e-learning practice from developing" (page 153 on my printed version but just before the conclusion to chap.12 anyway!!). This is really not the way I, or any of my H800 tutor group, read activity theory. From reading Engeström I thought that contradictions were a necessary part of expansive learning and that they should be recognised and accepted in contrast to being contained, diverting the energy and losing the impetus for expansive learning.
I commented in the H800 forum that expansive learning presupposes that specific contradictions will give learners the impetus to solve them but that Engeström does not address the fact that the subject may decide to avoid any conflict or stress by remaining with the current situation. In order to retain the impetus for expansive learning, the lecturers should be supported to work through contradictions. They may benefit from support in learning new technologies and policy changes that recognise the extra work involved in creating, developing and running accessible e-modules.