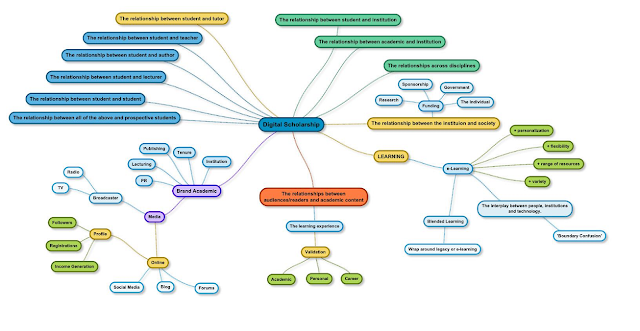
Why does the OU put the novice and expert together in the MAODE?
Although I praise this approach and after two years have been a beneficiary I wonder if the research points to the need for greater flexibility and mixing, more akin to several cohorts of students being able to move around, between their own tutor group, contributing to discussions with the newcomers while also being able to hobnob with the experts?
The learning theory that I am coming to understand does not favour a fixed approach.
It isn't simply a case of playing to the individual, though this is certainly very important as some people will favour being the teacher or the taught, or simply relish periods when they sit at the feet of the expert or stand up in front of newcomers. Rather it is apparent that people learn well within a peer group of like-minds, with people at a similar stage to themselves while having planned opportunities to hear and participate with 'great minds' while also from time to time contributing to the efforts and feeding off the enthusiasms of the 'new minds'.
Nothing is fixed, neither learning vicariously (Cox, 2006), or learning from the periphery to the centre (Seely Brown and Duguid, 1999).
Stage one of my approach to reading these days is to highlight, even share quotes and notes on Twitter as I go through a book.
I then type up my notes and add further thoughts either by cutting and pasting from the aggregates notes in my Twitter feed (eBooks don't allow you to cut and paste) or from handwritten notes I take on cards.
Then I share my notes here, tagged so that I can revisit and others can draw on my notes too or take the hint and read the chapter or book for themselves.
This too is but a stage - next step is to wrap up my developing thoughts, comments and other conversations and put a version of this entry into my external blog my mind bursts.
Sometimes an exchange here or elsewhere develops my thinking further - today I will be sitting down with a senior learning designer, one of five or six in the office of an international e-learning agency to talk learning theory and educational principles.
Chapter 2
Regarding Quality Assurance - there should be no inconsistencies between:
- Curriculum
- Teaching methods
- Learning environment
- Assessment procedures
So align assumptions:
- Learning outcomes
- Suitable assessment
N.B. Each outcome requires a different kind of theoretical perspective and a different pedagogical approach. L757
(Easy to say in theory, not so easy to deliver in practice?)
Three clusters of broad perspectives:
- Associationism
- Behaviourism
- Connectionism
Associationist: gradual building of patterns of associations and skill components. Therefore activity followed by feedback.
Simple tasks prerequisites to more complex.
Gagné (1985 and 1992)
- Instructional task analysis of discrimination, classifications and response sequences.
- Simpler tasks built step by step followed by coordination to the whole structure.
Instructional Systems Design
- Analyse the domain into a hierarchy of small units.
- Sequence the units so that a combination of units is not taught until its component units are grasped individually.
- Design an instructional approach for each unit in the sequence.
Then add:
- Immediate feedback
- Individualization of instruction
Behaviourism: active learning by design. Immediate feedback on success, careful analysis of learning outcomes, alignment of learning objectives.
The Cognitive Perspective
- Attention
- Memory
- Concept Formation
Knowledge acquisition as the outcome of an interaction between new experiences and the structures for understanding that have already been created. Therefore building a framework for learning vs. learning as the strengthening of associations.
Piaget (1970) Constructivist Theory of Knowledge.
‘Conceptual development occurs through intellectual activity rather than by the absorption of information'. L819
Vygotsky (1928:1931) Importance of social interaction.
Interactions – that e-learning teams call ‘interactivities’.
The Situative Perspective
- Learning must be personally meaningful
- Authentic to the social context
(problem-based learning and cognitive apprenticeship). L862
The concept of community practice
Wenger (1998) identify as a learner derived from the community. (Aspires, defines, accredited).
Mayes et al (2001) learning through relating to others. E.g. Master Class
Social-anthropological belonging to the community. L882.
Beliefs, attitudes, common endeavour, also ‘activity systems’ Engestrom 1993
Learning relationships
Identify, participate, individual relations. Dependent on: context, characteristics and strength of relationships in the group (Fowler and Mayes, 1999) L902
What was exotic in 2007 in common place today?
See Appendix 1 L912
Learning as a cycle through stages.
- J F Vernon (2011) H809 assignments and end of module assessment. The concept of riding a thermal of gently rising circles.
- Various references L923.
- Fitts and Posner (1968)
- Remelhart and Norman (1978)
- Kolb (1984)
- Mayes and Fowler (1999)
- Welford (1968)
If ‘as it proceeds from service to expert, the nature of learning changes profoundly and the pedagogy based on one stage will be inappropriate for another’. L923
Fowler and Mayes (1999)
Primary: preventing information
Secondary: active learning and feedback
Tertiary: dialogue and new learning.
REFERENCE
Beetham, H and Sharpe, R. (2007) Rethinking Pedagogy for a Digital Age: Designing and delivering e-learning.
Cole, M and Engestrom, Y (1993) A cultural-historical approach to distributed cognition. In G.Salmon (ed.) Distributed cognitions: Psychological and Educational Considerations, New York, CVP.
Cox, R. (2006) Vicarious Learning and Case-based Teaching of Clinical Reasoning Skills (2004–2006) [online], http://www.esrcsocietytoday.ac.uk/ esrcinfocentre/ viewawardpage.aspx?awardnumber=RES-139-25-0127 [(last accessed 10 March 2011).
Gagné, R (1985) The conditions of learning. New York. Holt, Rhinehart and Wilson.
Jonassen, D.H. and Rohrer-Murphy, L (1999) ‘Activity theory as a framework for designing constructivist learning environments’. Educational Technology Research and Development, 47 (1) 61-80
Seely-Brown, J.S and Duguid, P. (1991) ‘Organizational learning and communities-of-practice: toward a unified view of working, learning and innovation’, Organizational Science, 2 (1): 40-57